aunt — Auto Unattend¶
aunt automatise l’installation de Windows avec AutoUnattend.xml et réduit la taille des images.
Utilisation¶
aunt -h affiche l’aide, aunt sans argument vérifie les dépendances puis affiche l’aide :
usage: aunt [-h] [-aimnqvy] [-e ED] [-k KEY] [-l LANG] [-p NAME] [-s SUF] ISO [FILE] ...
Auto Unattend 0.3
positional arguments:
ISO Windows.iso to be automated
FILE ... include custom files and directories
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-a, --all flags -mny
-e ED, --edition ED Core, CoreN, Professional... not -e: registry
-i, --inplace rewrite ISO
-k KEY, --key KEY auto-activate... not -k: limited features
-l LANG, --lang LANG en-US, fr-FR... not -l: lang.ini
-m, --microsoft no Microsoft account
-n, --network no network setup
-p NAME, --pc NAME computer name... not -p: PC
-q, --quiet no output
-s SUF, --suffix SUF append to ISO name... not -s: _
-v, --verbose detail actions in bash syntax
-y, --yes accept license
aunt Windows.iso réécrit le *.iso UDF amorçable et affiche les étapes :
extract Windows.iso to _tmp
query EditionID
read lang.ini
read boot.wim
reduce boot.wim
read install.esd
reduce install.esd
write AutoUnattend.xml
write Windows.iso
delete _tmp
aunt -v Windows.iso détaille les actions en syntaxe bash, les mots grep mv rm sont pratiques pour comprendre ce qui se passe, bien que ces actions soient écrites en Python pur :
find dependencies
C:\Program Files\7-Zip\7z.exe
C:\Windows\System32\dism.exe
C:\Program Files\Quix0\oscdimg.exe
extract Windows.iso to _tmp
7z x -y -o_tmp Windows.iso bootmgr{,.efi} boot\{bcd,bood.sdi,bootfix.bin,etfsboot.com} efi\microsoft\boot\{bcd,efisys.bin} sources\{boot.wim,compres.dll,install.esd,lang.ini,setup.exe}
query EditionID
reg query 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion' /v EditionID
= Core
read lang.ini
grep -Eom1 '^([a-z]{2}-[a-zA-Z]{2}) ' lang.ini
= fr-fr
read boot.wim
dism /Get-WimInfo /WimFile:boot.wim
reduce boot.wim
dism /Export-Image /SourceImageFile:boot.wim /SourceIndex:2 /DestinationImageFile:boot.wim_
mv boot.wim_ boot.wim
read install.esd
dism /Get-WimInfo /WimFile:install.esd
reduce install.esd
dism /Export-Image /SourceImageFile:install.esd /SourceIndex:1 /DestinationImageFile:install.esd_
mv install.esd_ install.esd
write AutoUnattend.xml
write Windows_.iso
oscdimg -u2 -bootdata:2#p0,e,b_tmp\boot\etfsboot.com#pEF,e,b_tmp\efi\microsoft\boot\efisys.bin _tmp Windows_.iso
delete _tmp
rm -r _tmp
Les commandes dism ci-dessus suppriment toutes les éditions de Windows autres que celle choisie par l’option -e. Sans -e suppose que l’édition désirée est la même que EditionID de l’hôte.
Il est possible d’inclure des fichiers et dossiers personnels dans l’ISO:
aunt Windows.iso ExecTI.exe python-3.7.2-amd64.exe
-a équivaut à -mny, ce qui génère un AutoUnattend.xml comme ci-dessous :
<?xml encoding="utf-8"?>
<unattend>
<settings pass="WindowsPE">
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-International-Core-WinPE" ...>
<UILanguage>fr-fr</UILanguage>
</component>
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Setup" ...>
<ImageInstall>
<OSImage>
<InstallFrom>
<MetaData>
<Key>/IMAGE/INDEX</Key>
<Value>1</Value>
</MetaData>
</InstallFrom>
</OSImage>
</ImageInstall>
<UserData>
<ProductKey>
<Key></Key>
</ProductKey>
<AcceptEula>true</AcceptEula>
</UserData>
</component>
</settings>
<settings pass="specialize">
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" ...>
<ComputerName>PC</ComputerName>
</component>
</settings>
<settings pass="OOBESystem">
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-International-Core" ...>
<SystemLocale>fr-fr</SystemLocale>
</component>
<component name="Microsoft-Windows-Shell-Setup" ...>
<OOBE>
<HideWirelessSetupInOOBE>true</HideWirelessSetupInOOBE>
<HideOnlineAccountScreens>true</HideOnlineAccountScreens>
</OOBE>
</component>
</settings>
</unattend>
État de sortie :
0: succès 1: fichier manquant 2: édition manquante dans le fichier d’image
Écrans¶
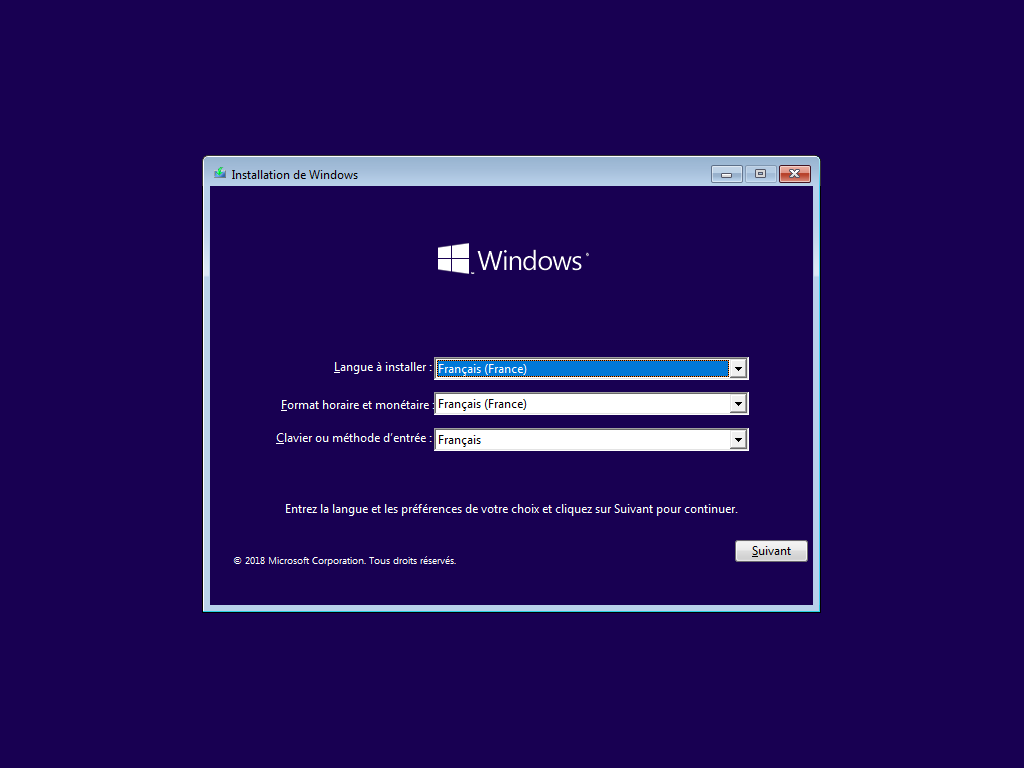
Écran caché, --lang ou lang.ini définit la langue :
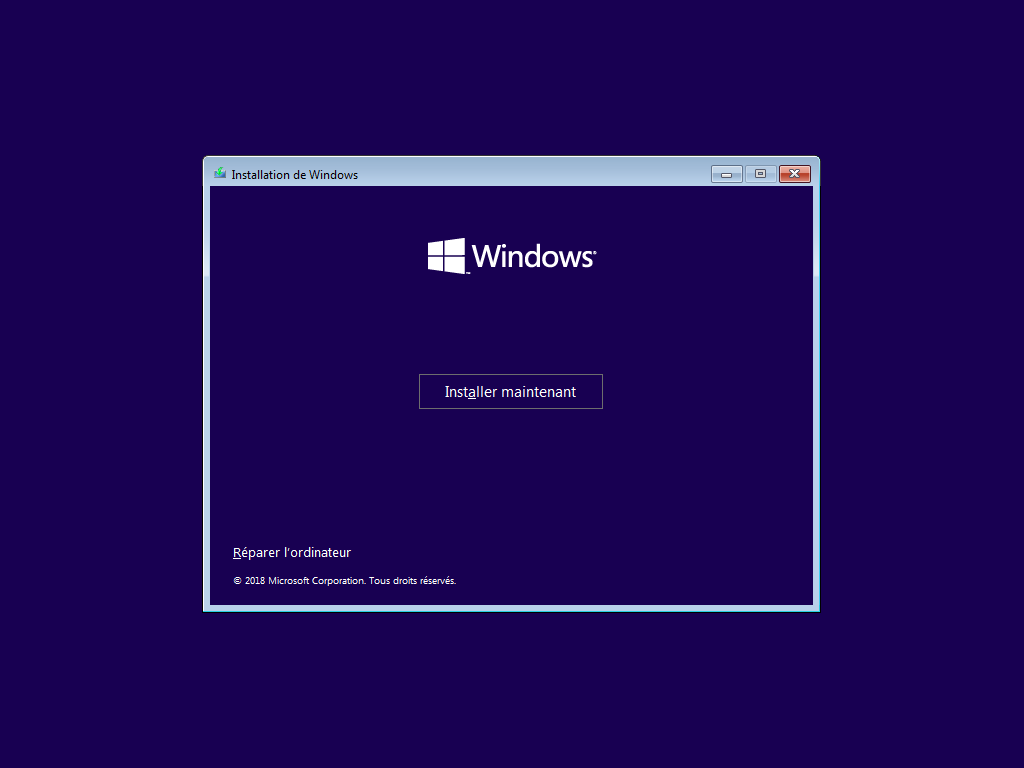
Écran caché :
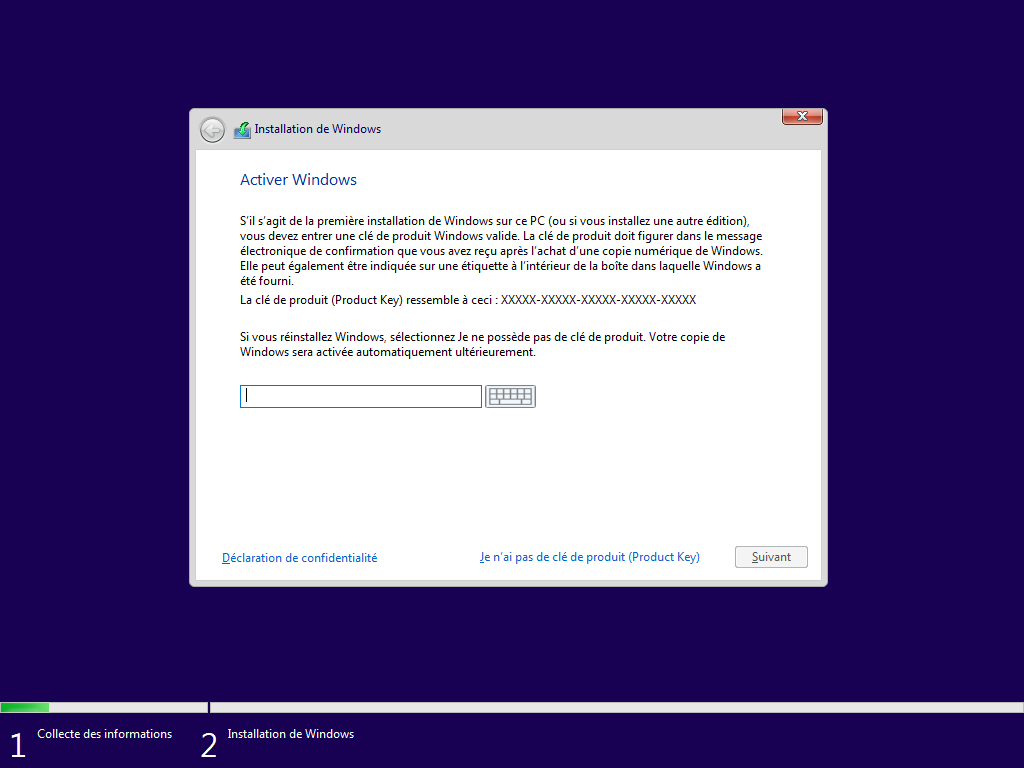
Écran caché, --key définit la clé d’activation sinon continue sans clé :
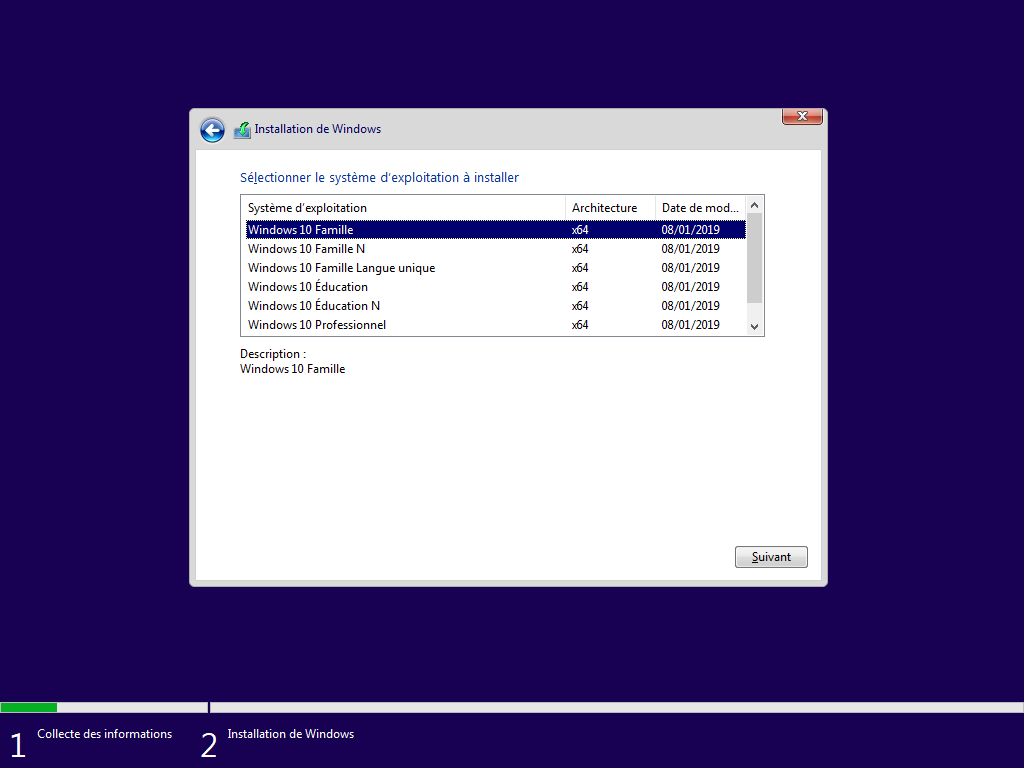
Écran caché, --edition ou EditionID de l’hôte définit l’édition de Windows :
--yes accepte la licence et cache cet écran :
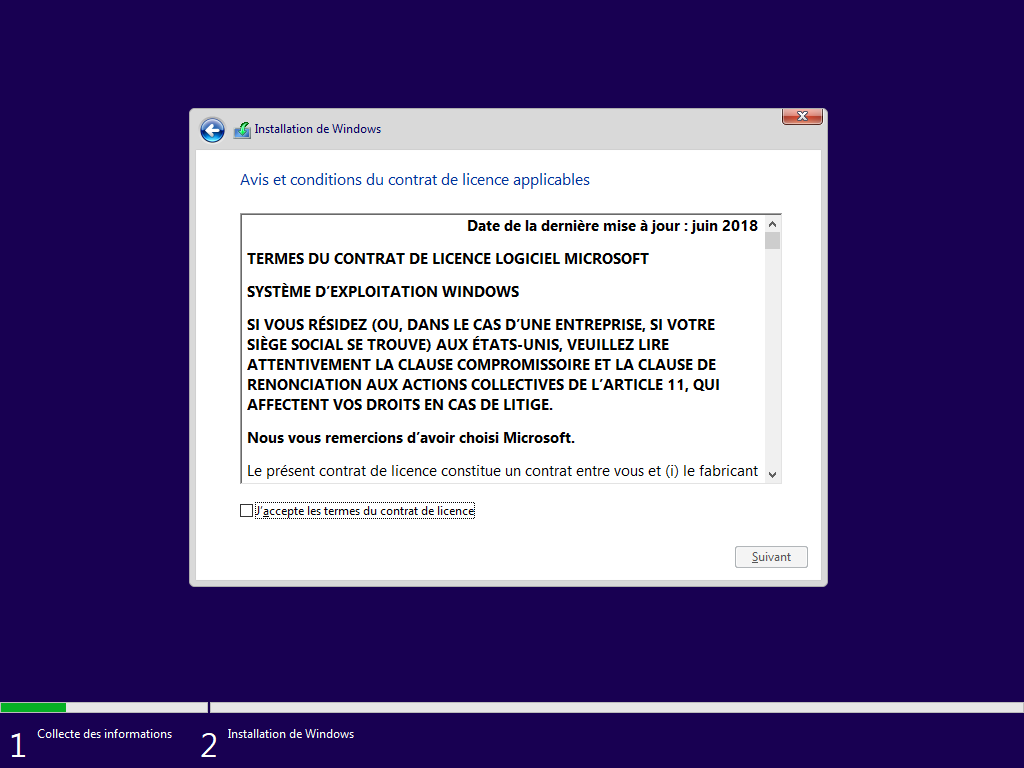
Écran caché, choisit l’installation « Personnalisée » :
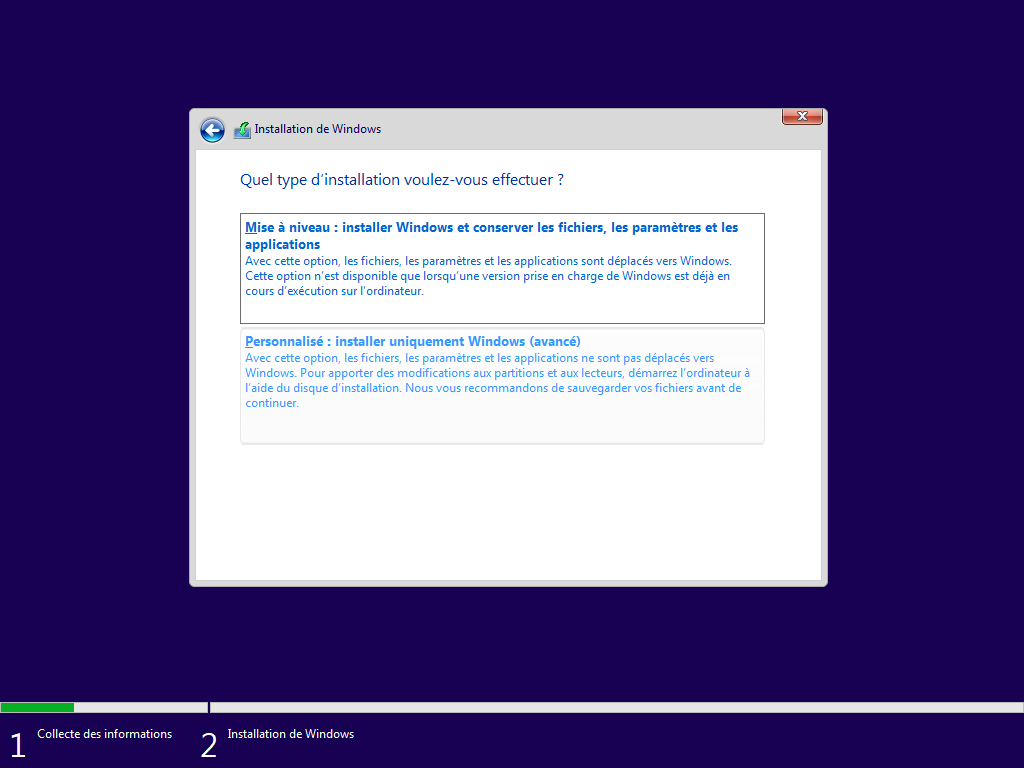
Affiché :
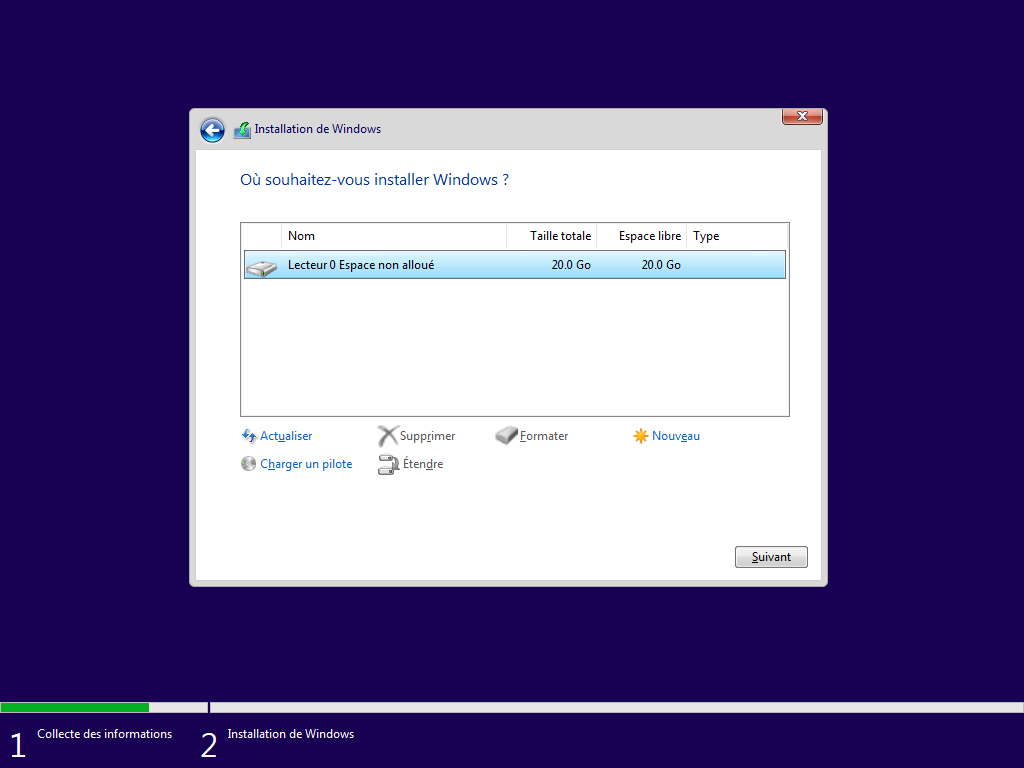
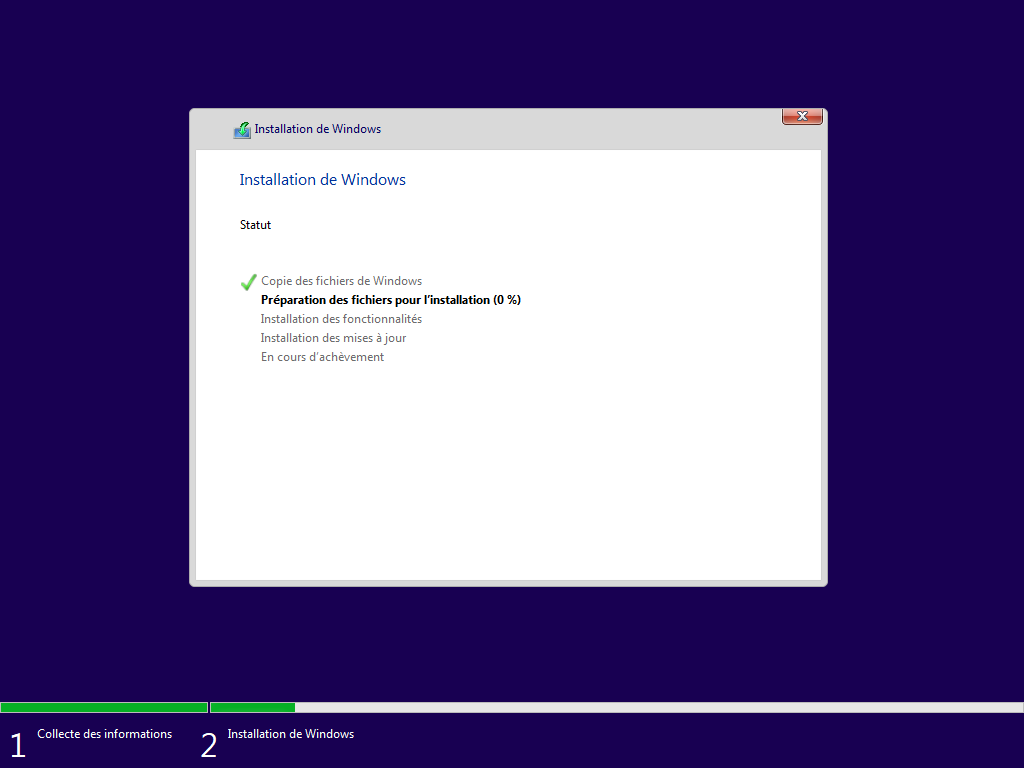
3 écrans cachés, --lang ou lang.ini définit la langue :
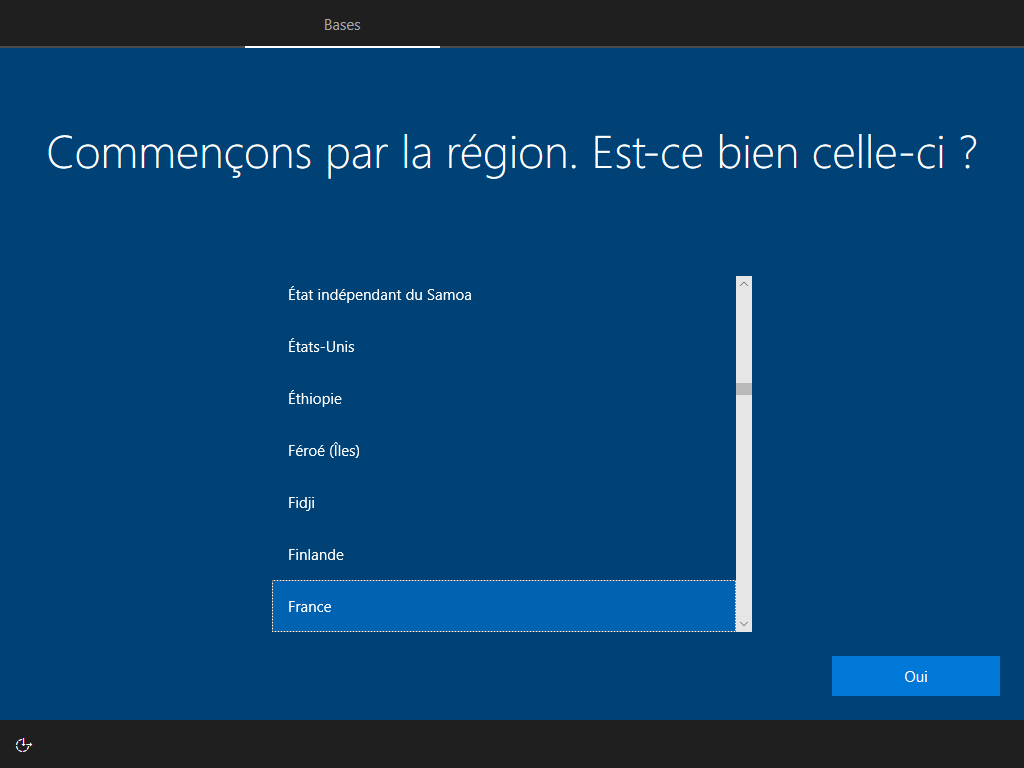
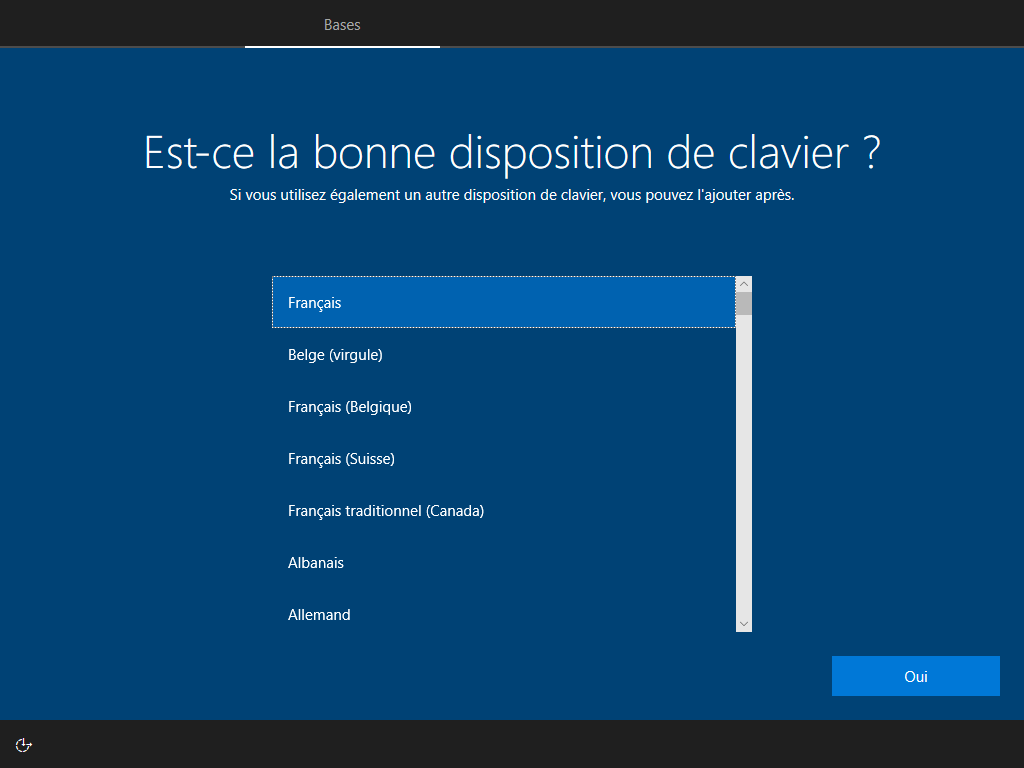
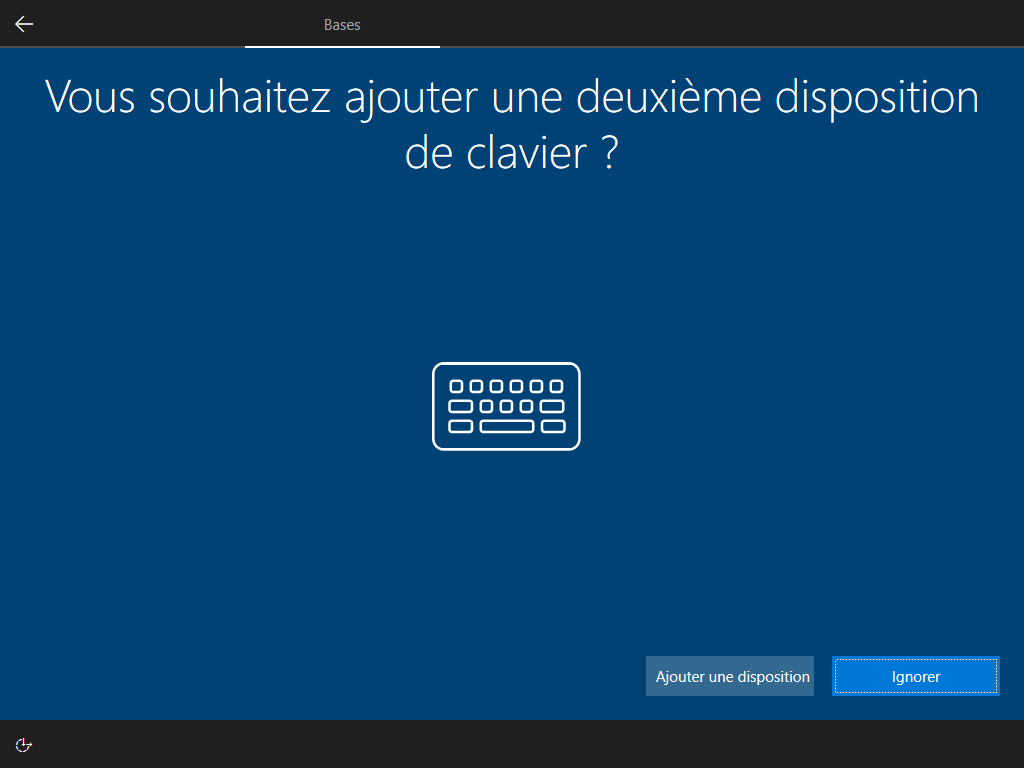
--network cache ces 2 écrans :
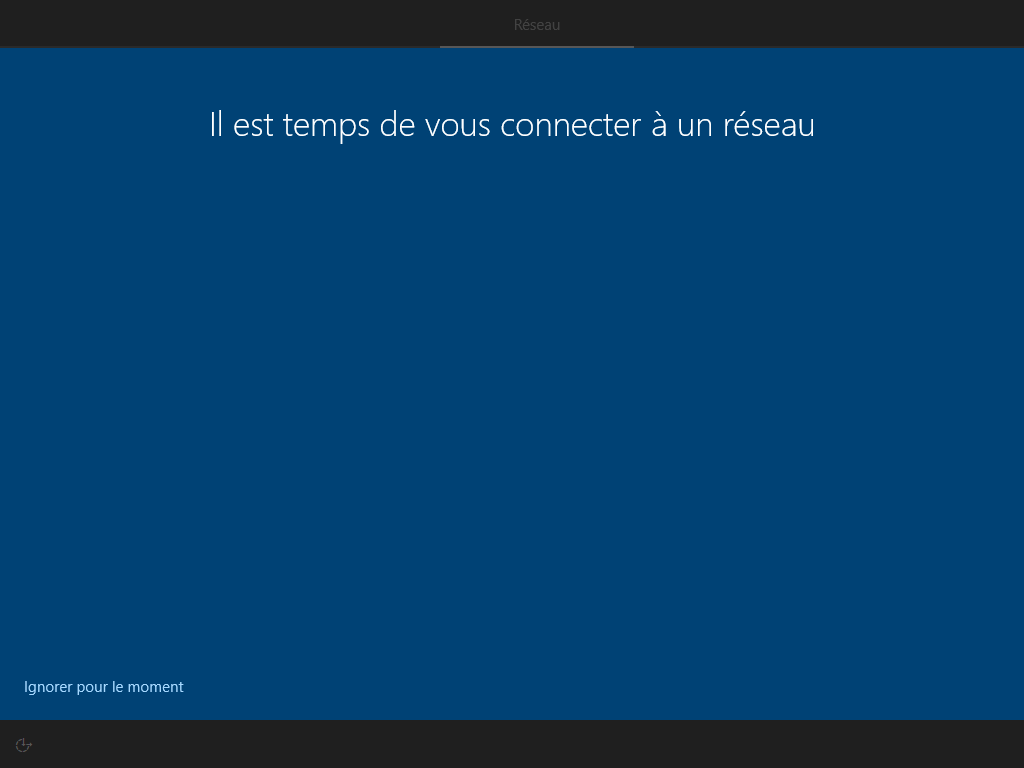
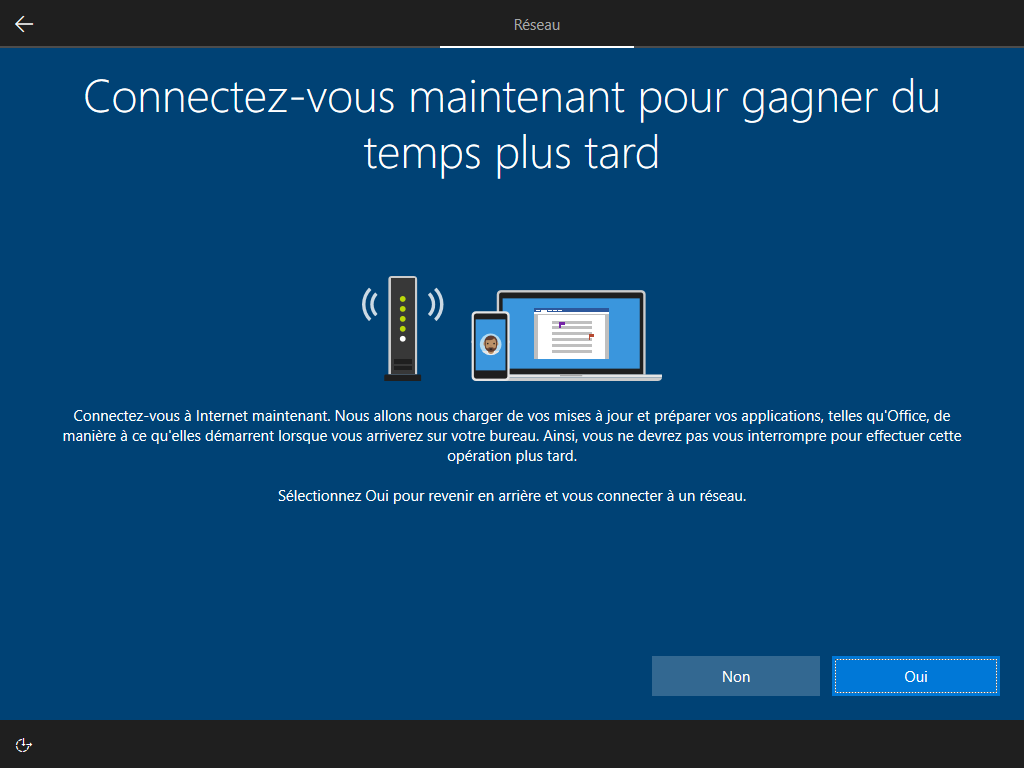
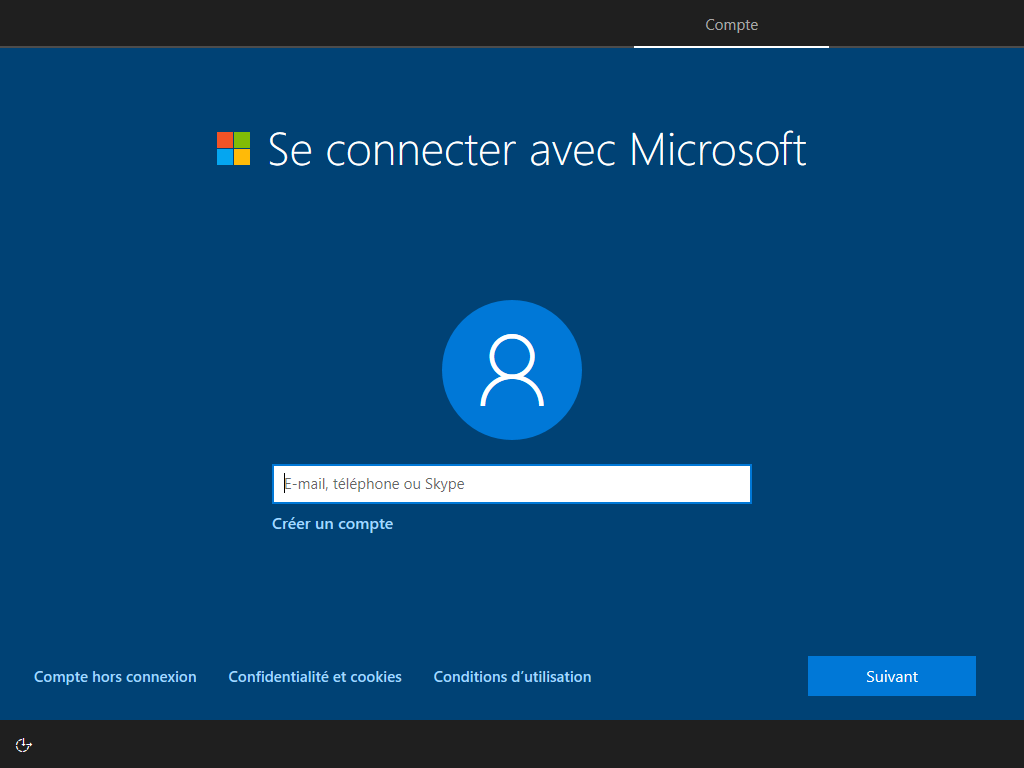
--microsoft cache ces 2 écrans :
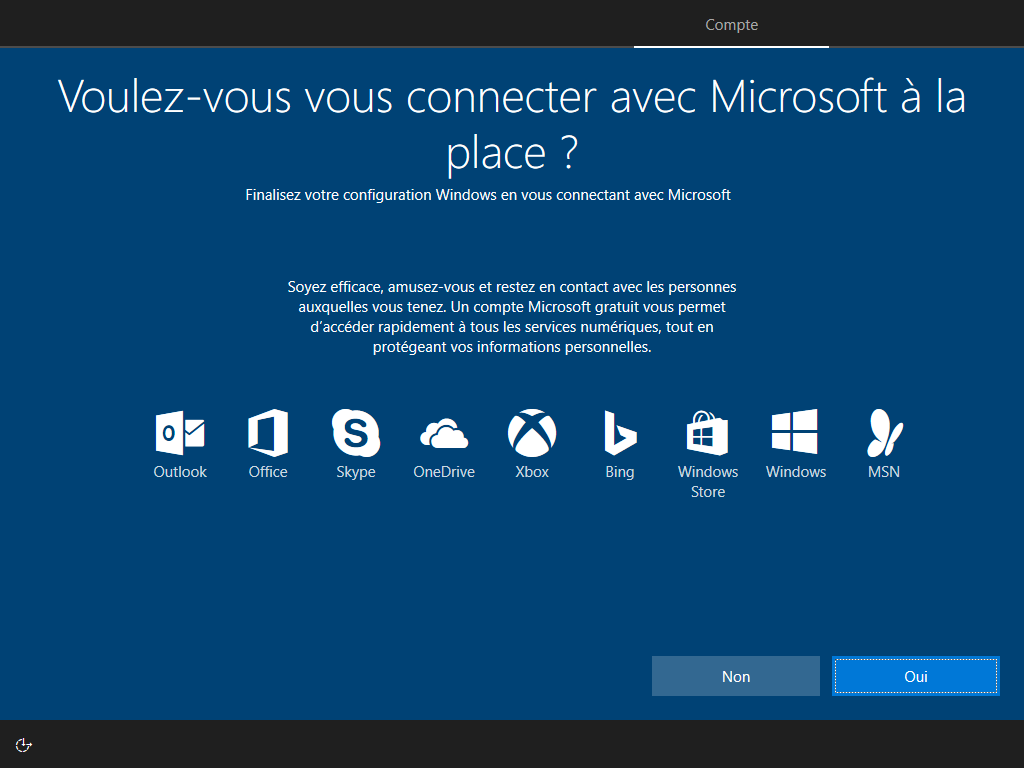
Affiché :
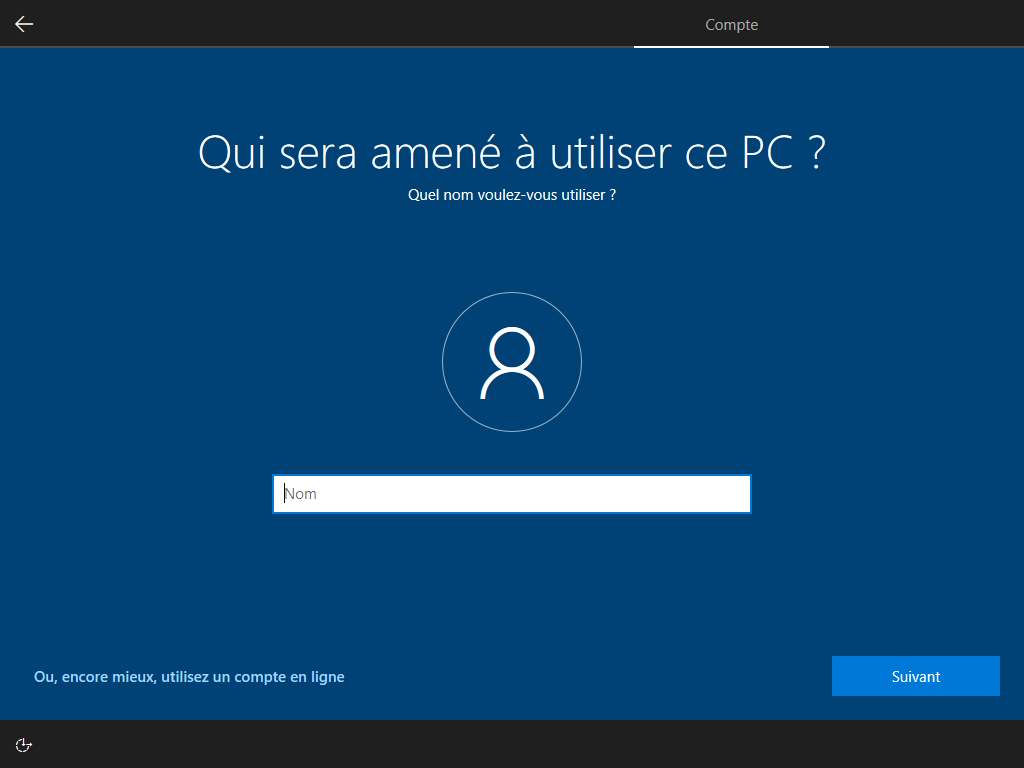
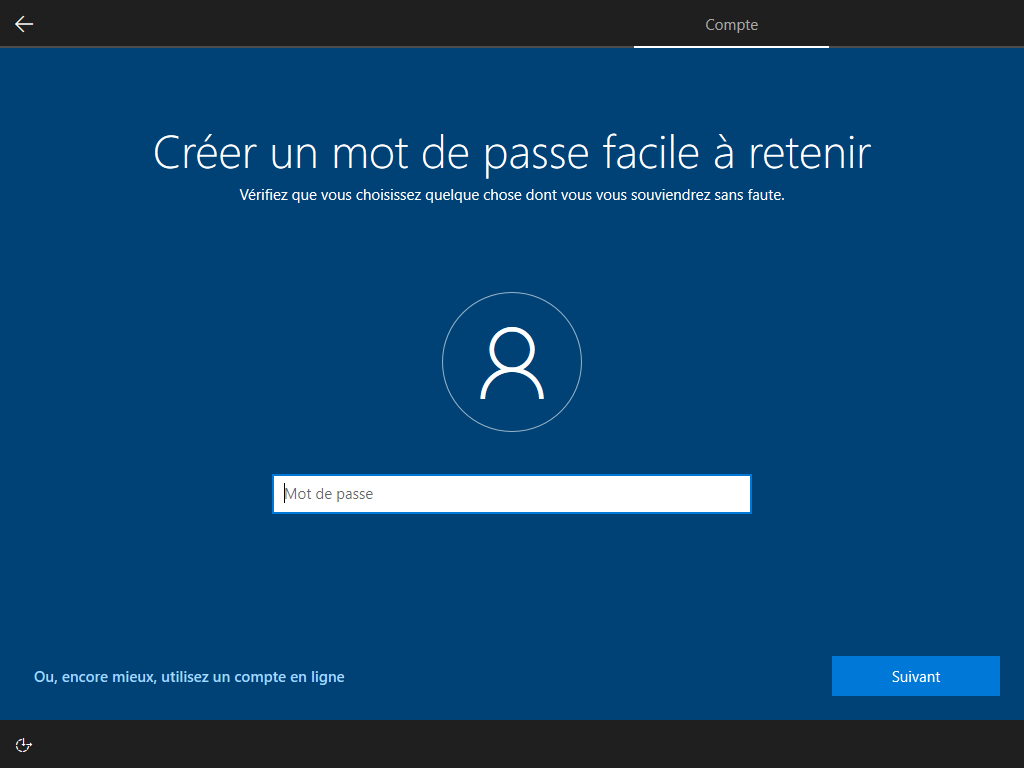
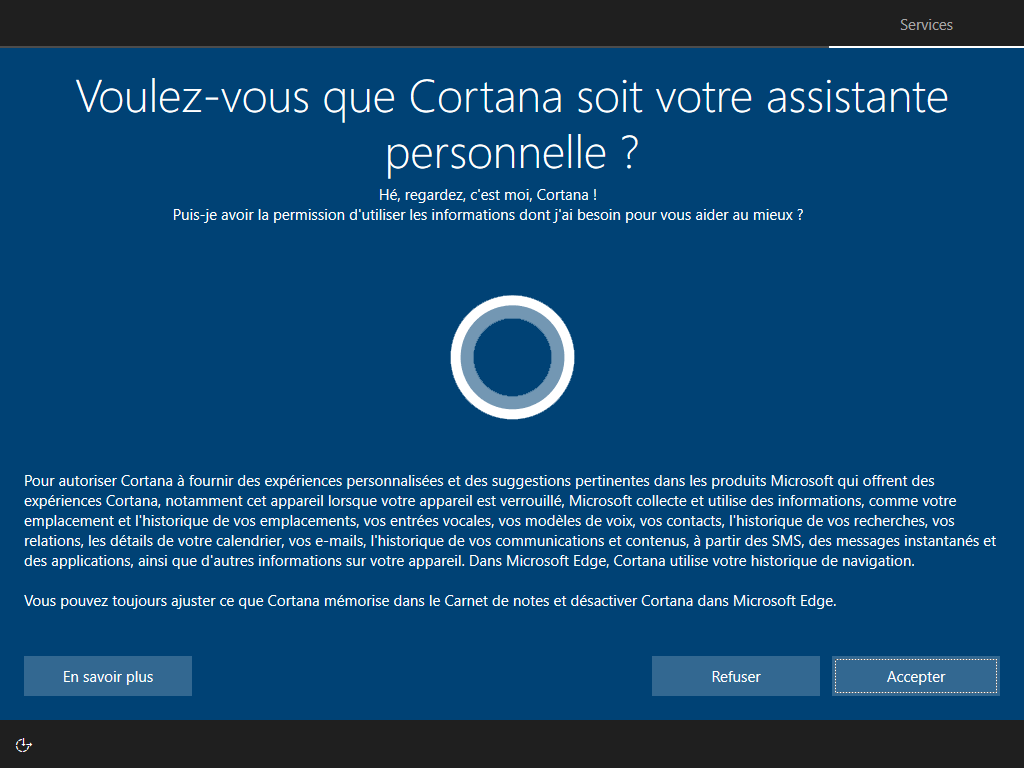
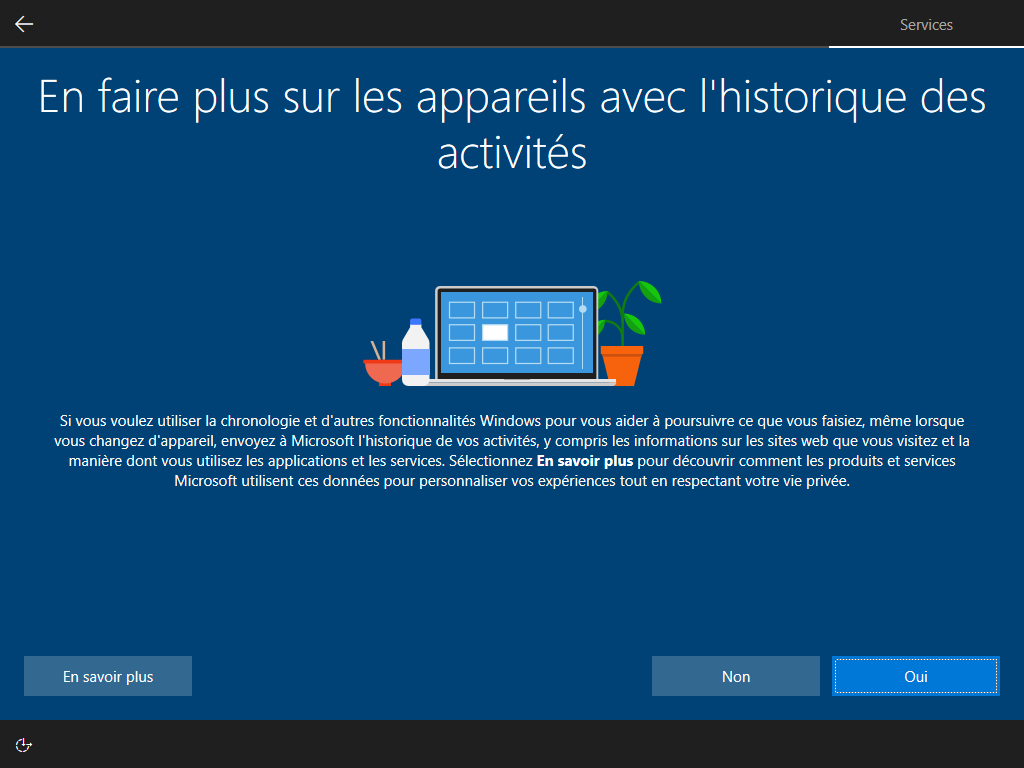
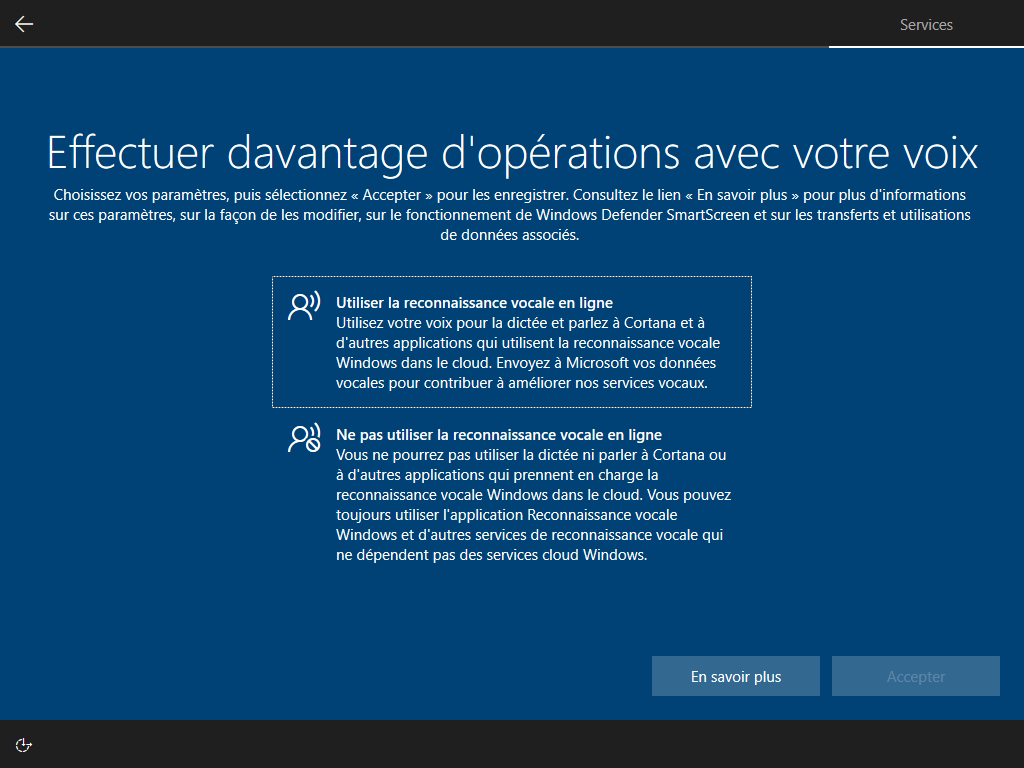
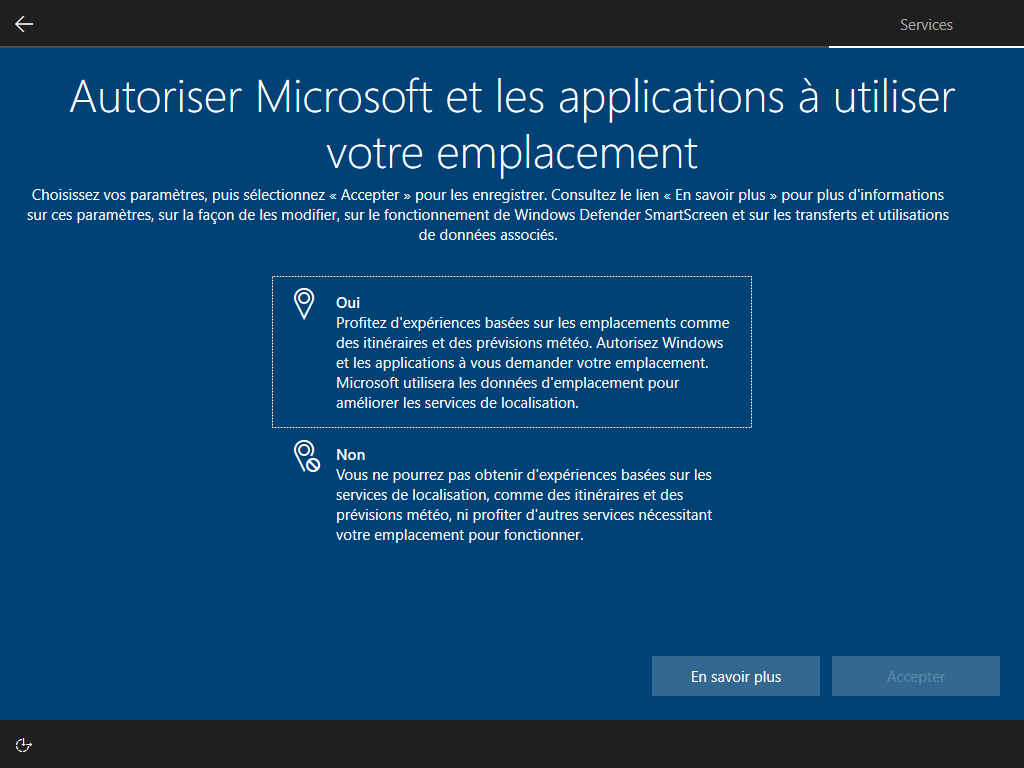
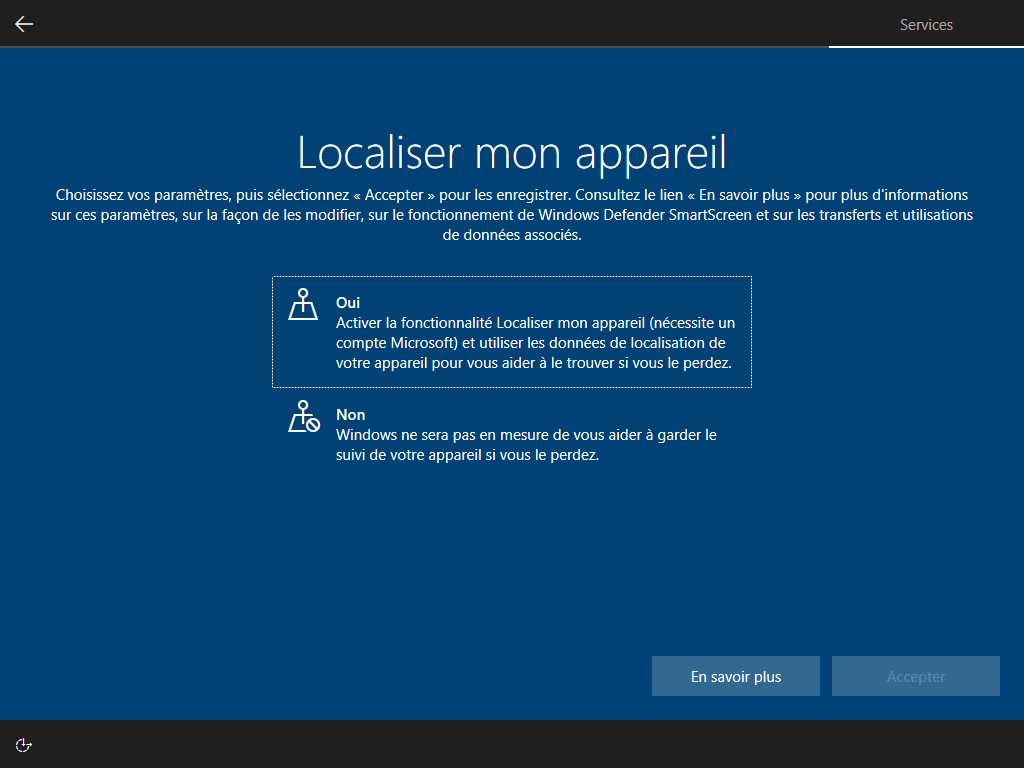
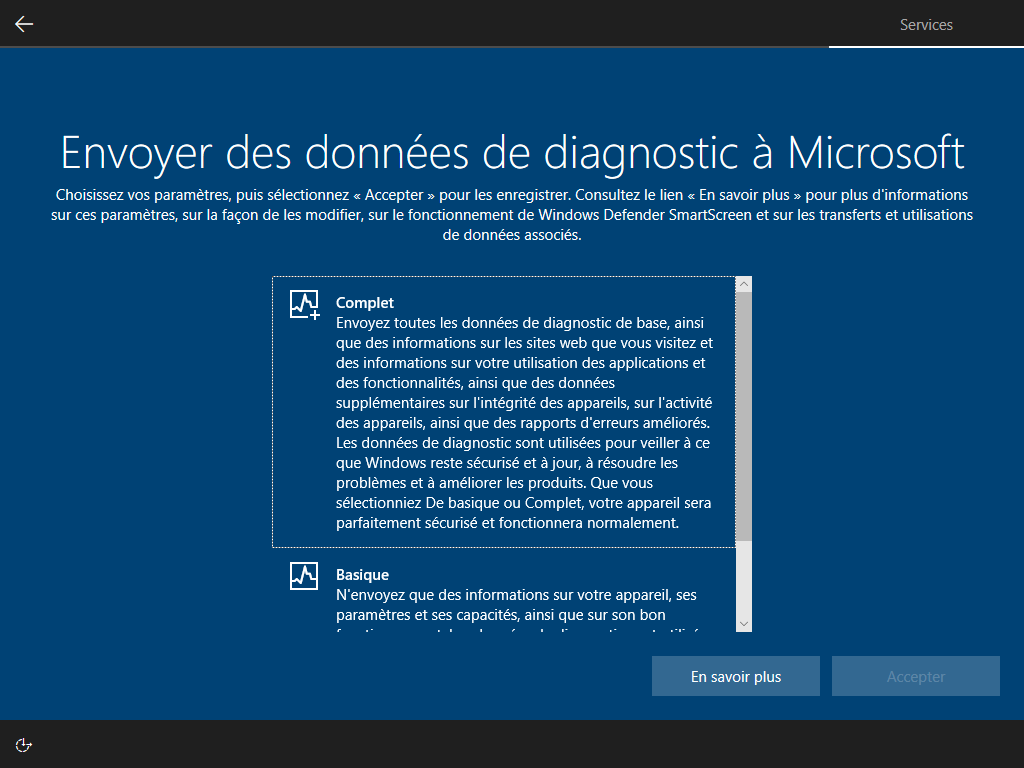
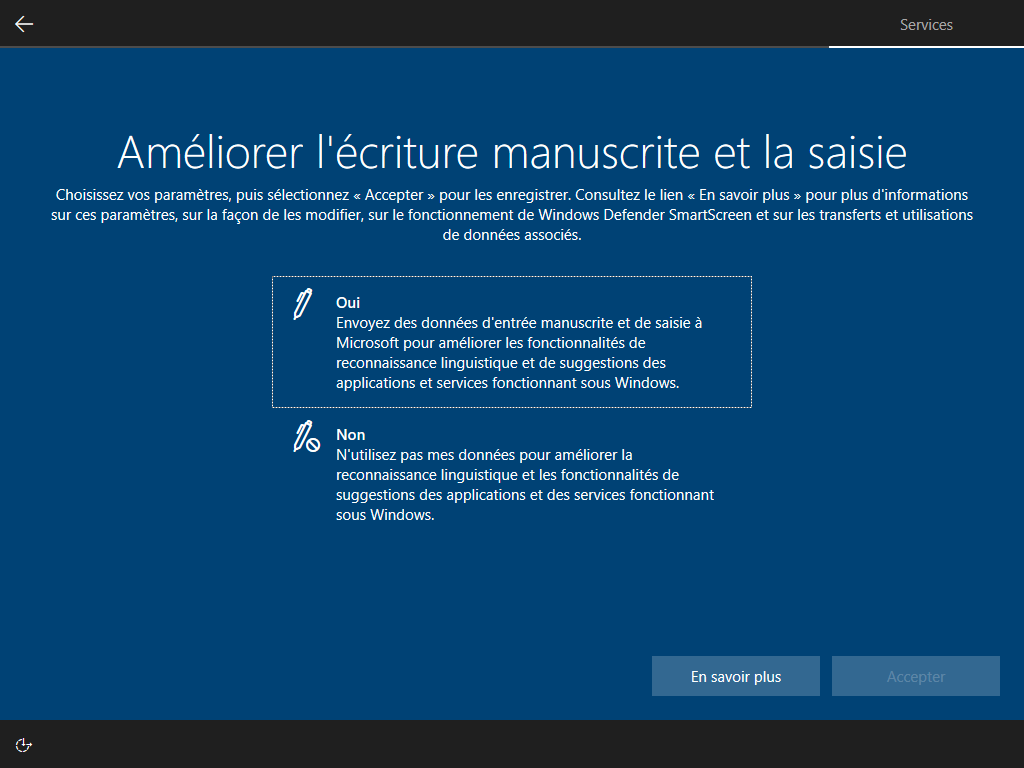
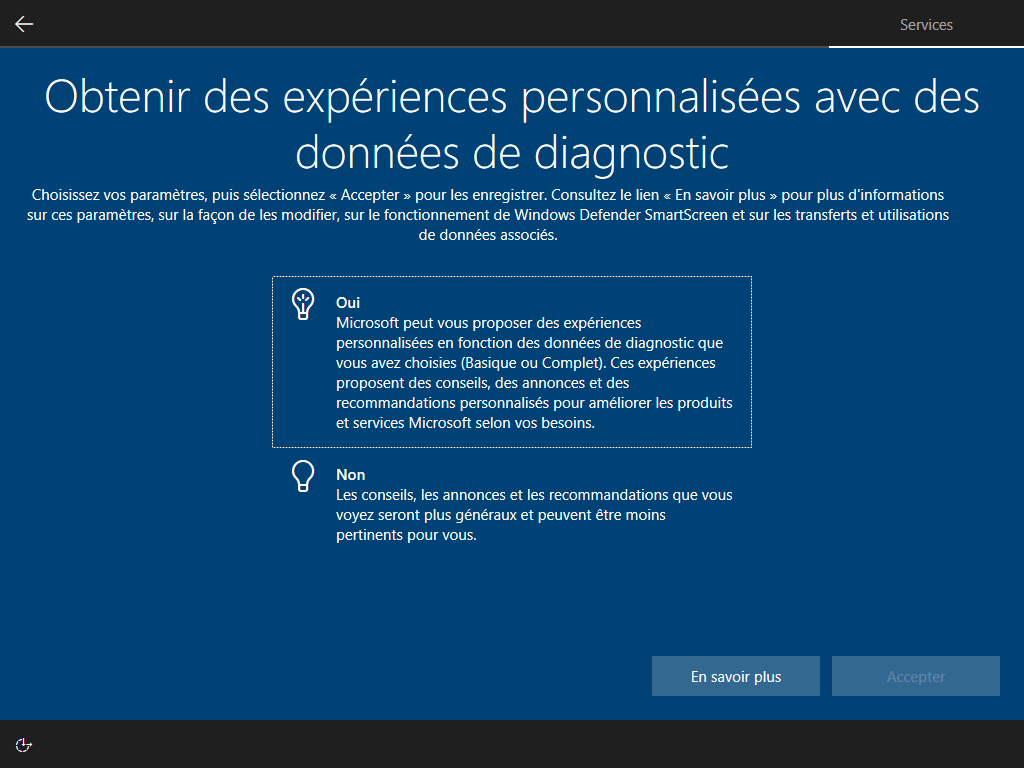
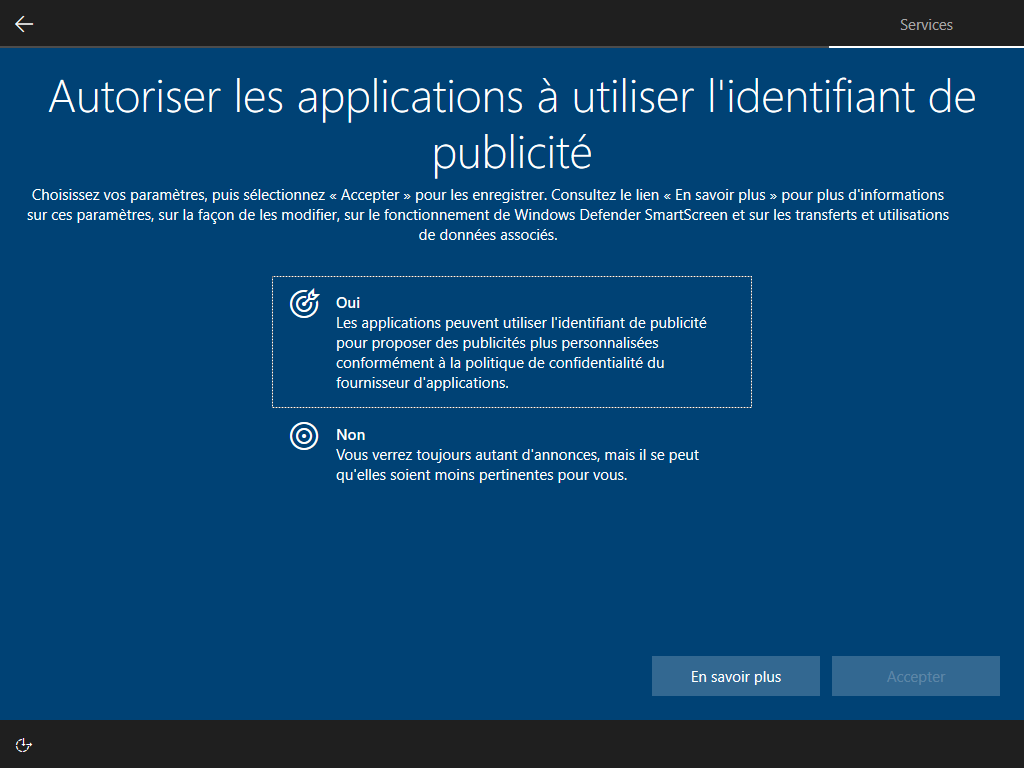
Écrire HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\EnableFirstLogonAnimation = 0 dans install.esd est le seul moyen de cacher cette animation, <FirstLogonCommands> s’exécute trop tard :

Tests¶
💿 Français x64 💿 Anglais x64 — Famille Pro Éducation [1] — VirtualBox 6 — VMware 15 :
| 1809: | 13 novembre 2018 — Redstone 5 |
|---|
| [1] | L’édition Éducation est l’édition Entreprise sans support à long terme |